The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesGreenhouse effect and explore natural and humancaused greenhouse gas emissions and their impacts Students will brainstorm and then research natural and human activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and draw them in a diagram Students then discuss how they can reduce their contributions to greenhouse gas emissions Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10
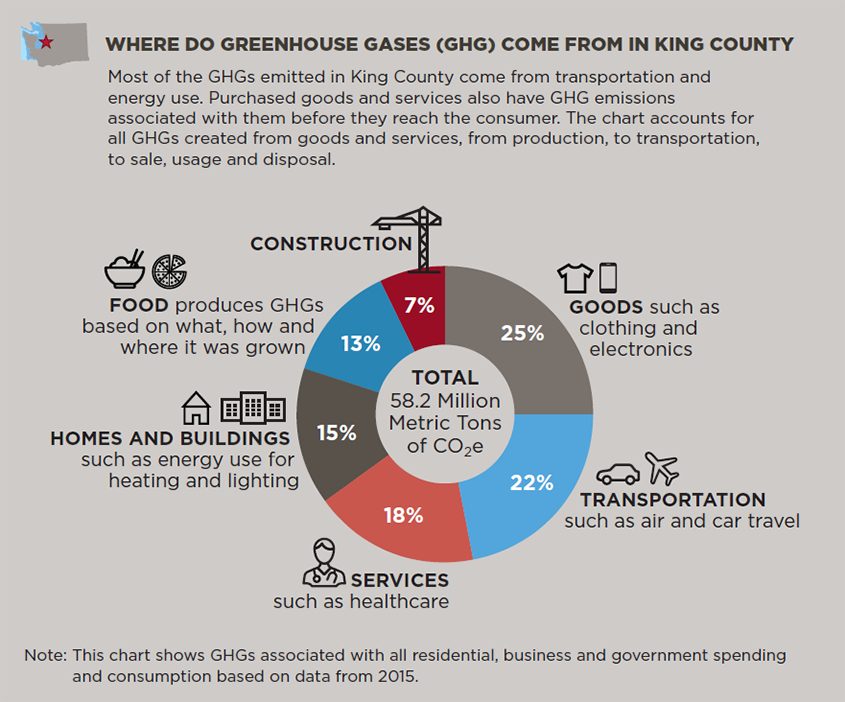
Greenhouse Gas Emissions In King County King County
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram-WHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of these gasesThe greenhouse gases 5 procedure, which is very similar to the way a greenhouse works, is the main reason why the In fact, the greenhouse effect would collapse gases that can produce this outcome are were it not for the presence of carbon dioxide collectively called as greenhouse gases
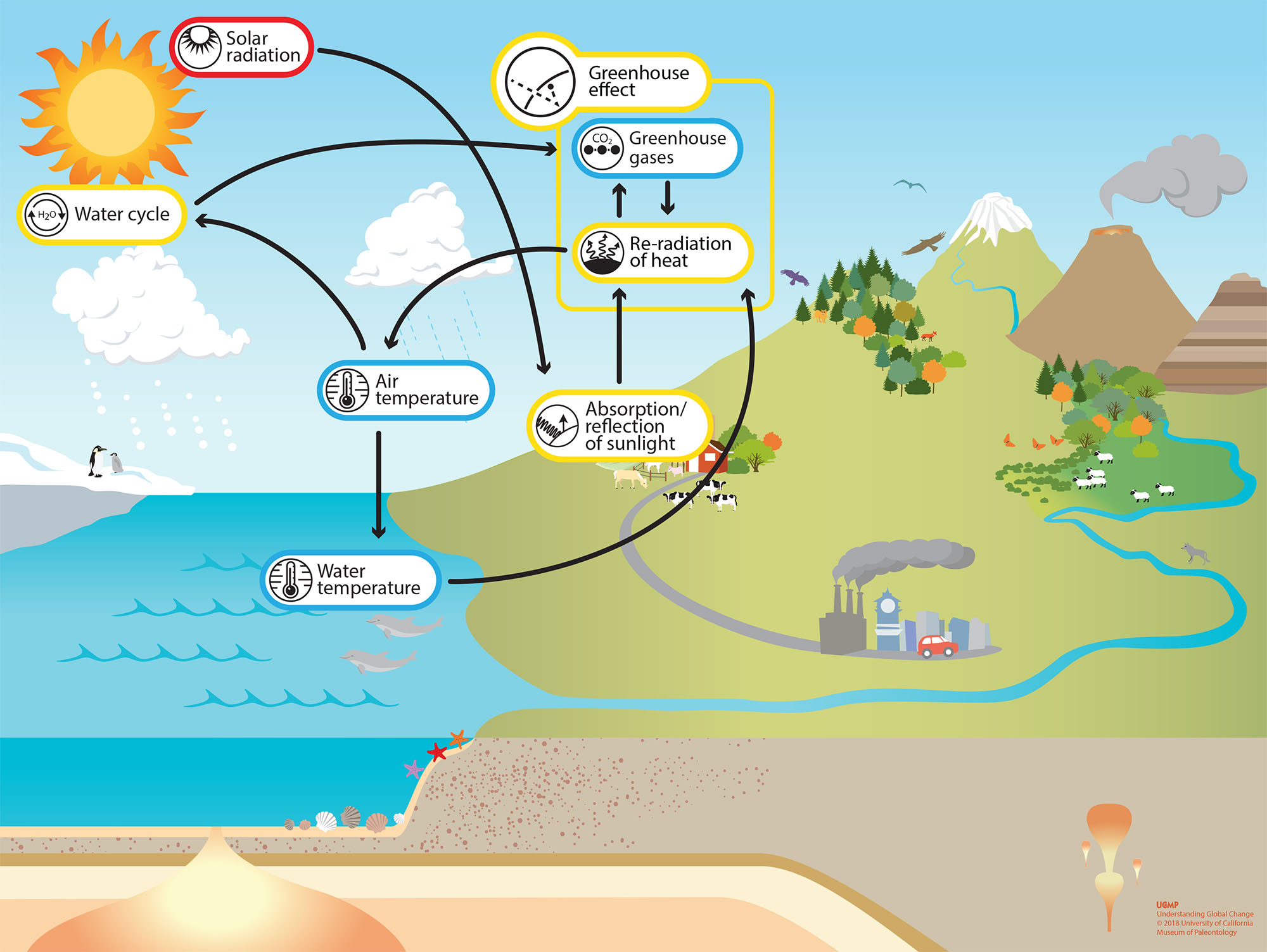



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change
Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases Greenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many yearsThe greenhouse effect has supported life on the earth for millions of years Today, however, the greenhouse effect is growing stronger as human activities such as deforestation and fossil fuel use release more and more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere This traps greater amounts of the sun's radiation, which contributes to rising temperatures, also known as global warming
The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works The Consequences of the Greenhouse Effect Today's humancaused greenhouse gas emissions are higher than ever, the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is rising rapidly, andThe effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations The natural greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space
Figure 71 Rise in the concentrations of greenhouse gases since the 18th century As we will see in section 73, simple theory shows that a rise in greenhouse gases should result in surface warming;& Human Sources of Greenhouse gases diagrams • Where do Greenhouse Gases Come From handouts • Greenhouse Gas Emissions Diagram handouts • Colored pencils National Science Education Standards D1h The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases that include water vapor Emissions For several greenhouse gases, the nation's estimated combined emissions that are directly attributable to human activity have increased 7 percent between 1990 and 14 Fossil fuel combustion is the country's major source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions Concentrations
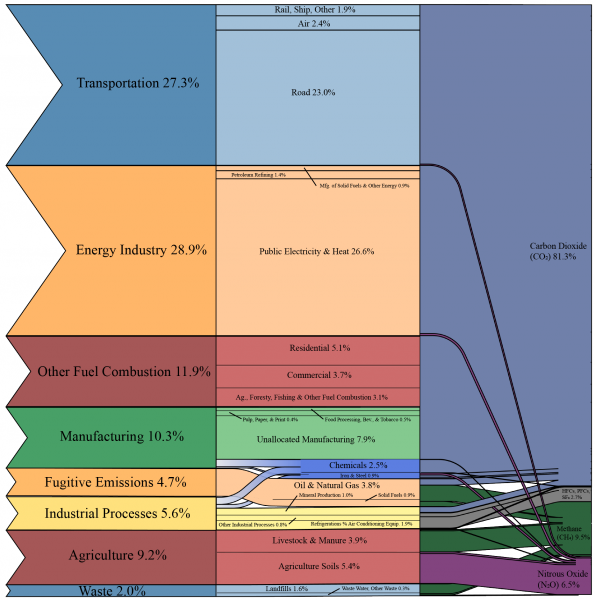



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on EarthA greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases This is called the " greenhouse effect " A diagram of the greenhouse effect Energy flows between space, the atmosphere, and Earth's surfaceThe rocks absorb heat from the sun, speeding up the melting process Many scientists use the term "climate change" instead of "global warming" This is because greenhouse gas emissions affect more than just temperature Another effect involves changes in precipitation like rain and snow




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In King County King County
The uncertainty lies in the magnitude of the responseIt is well established that the global mean surface temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century by about 06 K US emissions of greenhouse gases, based on global warming potential, 2 US greenhouse gas intensity and related factors, 3 Distribution of total US greenhouse gas emissions by enduse sector, 09 4 World energyrelated carbon dioxide emissions by region, 5 Greenhouse gases and 100year net globalTotal Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO2 equivalentPercentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding * Land Use, LandUse Change, and Forestry in the United States is a net sink and removes approximately 12 percent of these greenhouse gas emissions, this net sink is not shown in the above diagram




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
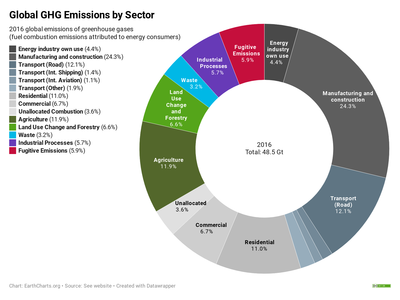



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
So the point is, according to the bottomup warming "greenhouse effect" hypothesis, an empty greenhouse should be considerably warmer than a full one, as attested to by the urban heat island effect, but this is not the case With regards to false analogies, try implementing cap and trade without using the words "greenhouse gas emissions"During a volcanic eruption, the main greenhouse gas that is emitted is carbon dioxide During an eruption, huge amounts of CO₂may be released (approximately 026 Gt/y globally), leading to an overall heating of the earth and its atmosphere through an accelerated greenhouse effect, often referred to as global warmingFor example, in 1991, Mount Pinotubo released over 05 Gt ofHow the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphere
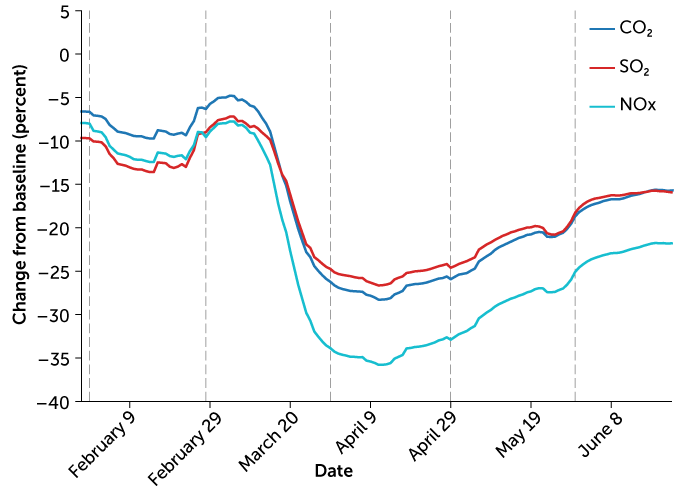



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
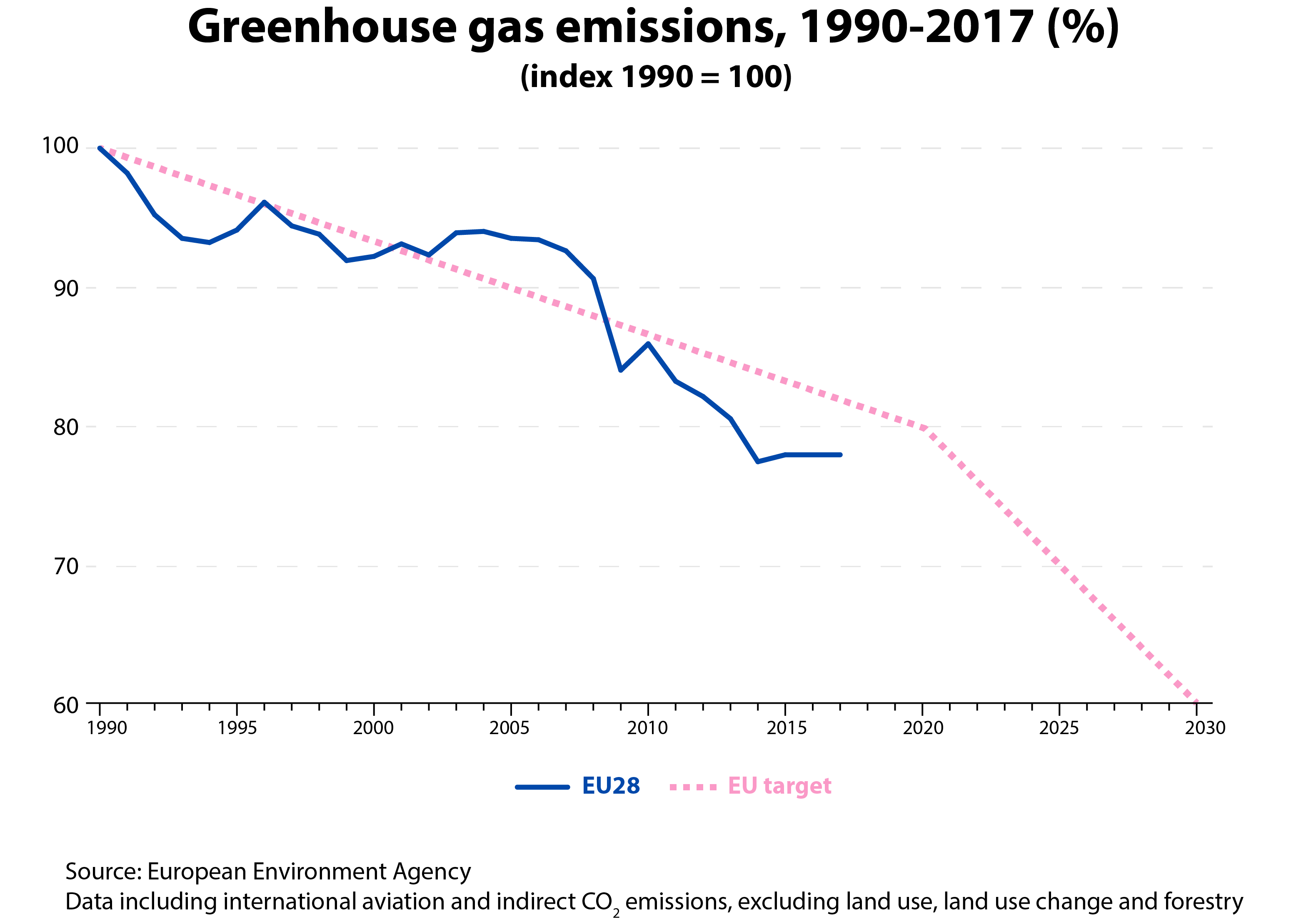



How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofIf you made our Gummy Greenhouse Gas models, you may wonder why the molecules you made with gumdrops are called greenhouse gases Here is why If the atmosphere contains too much of these gases, the whole Earth becomes a hotter and hotter greenhouse The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,
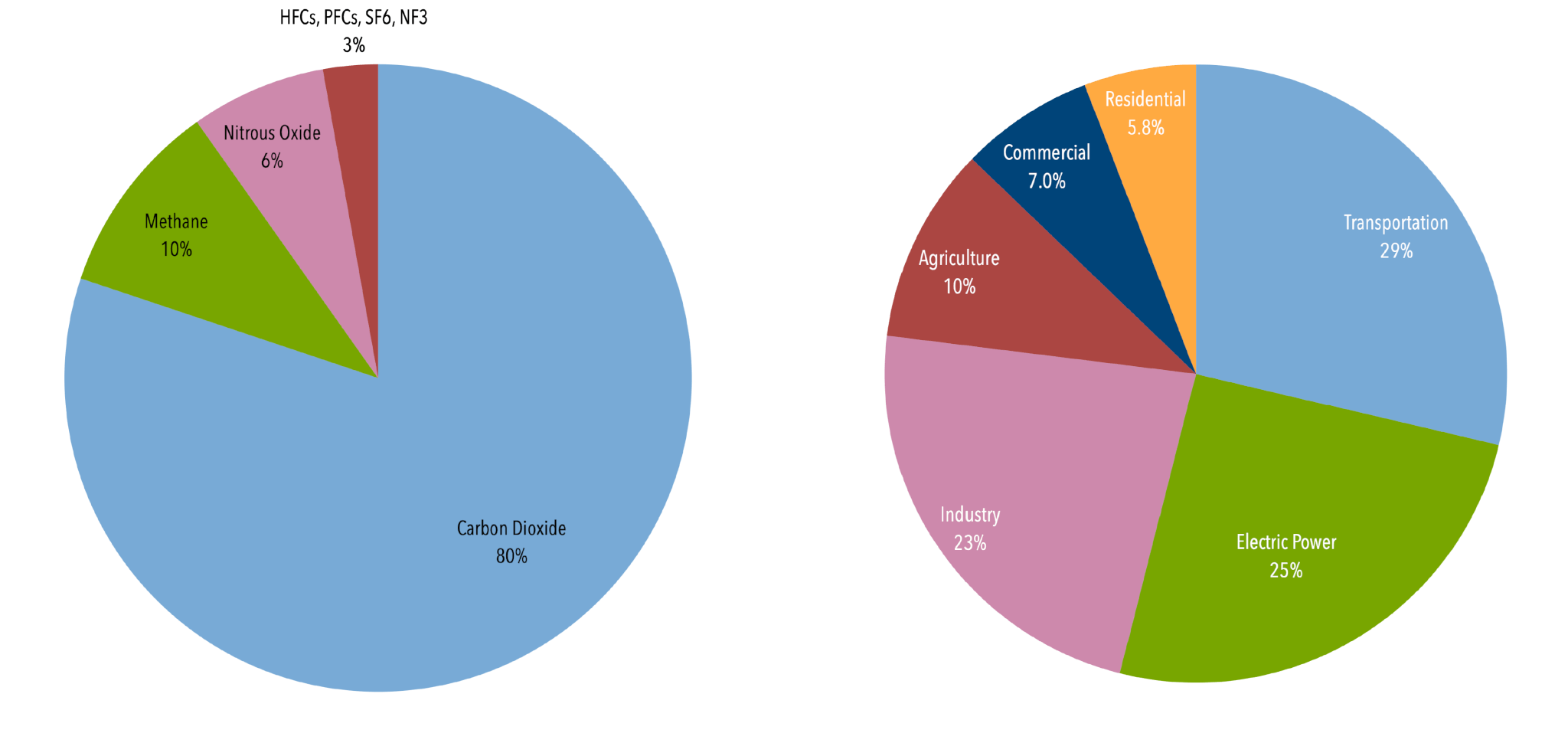



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



3
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouse gasesThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereTo the right is a diagram (also from NOAA, ESRL, the same source as the table above) which illustrates the greenhouse effect Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (round about the late 1700's), the concentration of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere has rocketed by an estimate of 30%, most significantly carbon dioxide




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions
"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlightThe Greenhouse Effect and Historical Emmissions Life as we know it is possible on Earth because of a natural greenhouse effect that keeps our planet about 60 o F warmer than it otherwise would be Water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2 ), and other trace gases, such as methane and nitrous oxide, trap solar heat and slow its loss by reradiation back to space
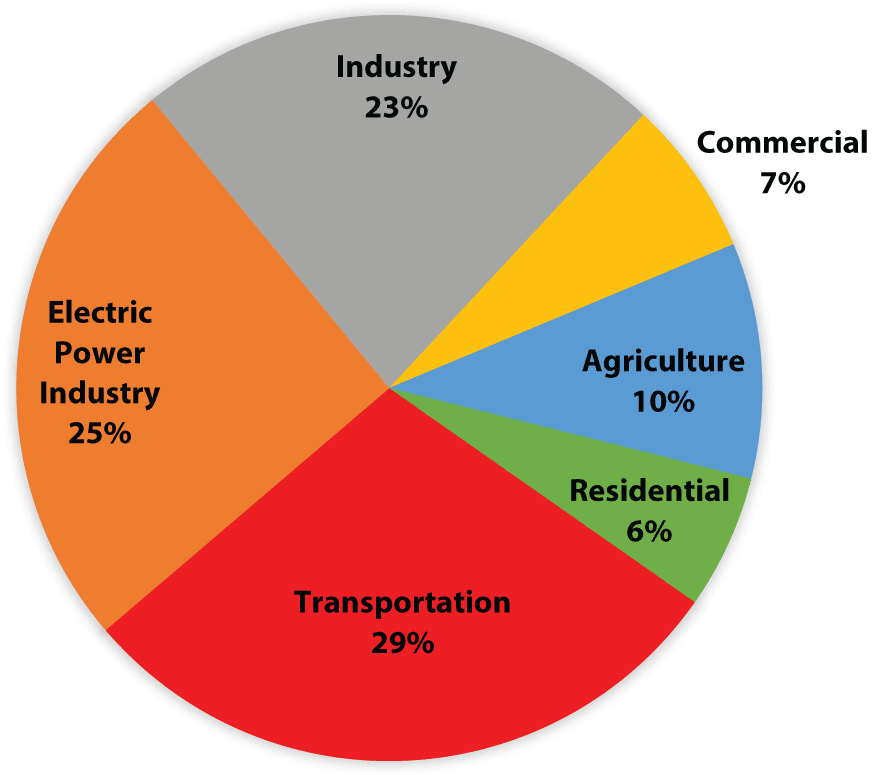



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Simple diagram of greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The main greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneIn our solar system, the atmospheres ofThis chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesA greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
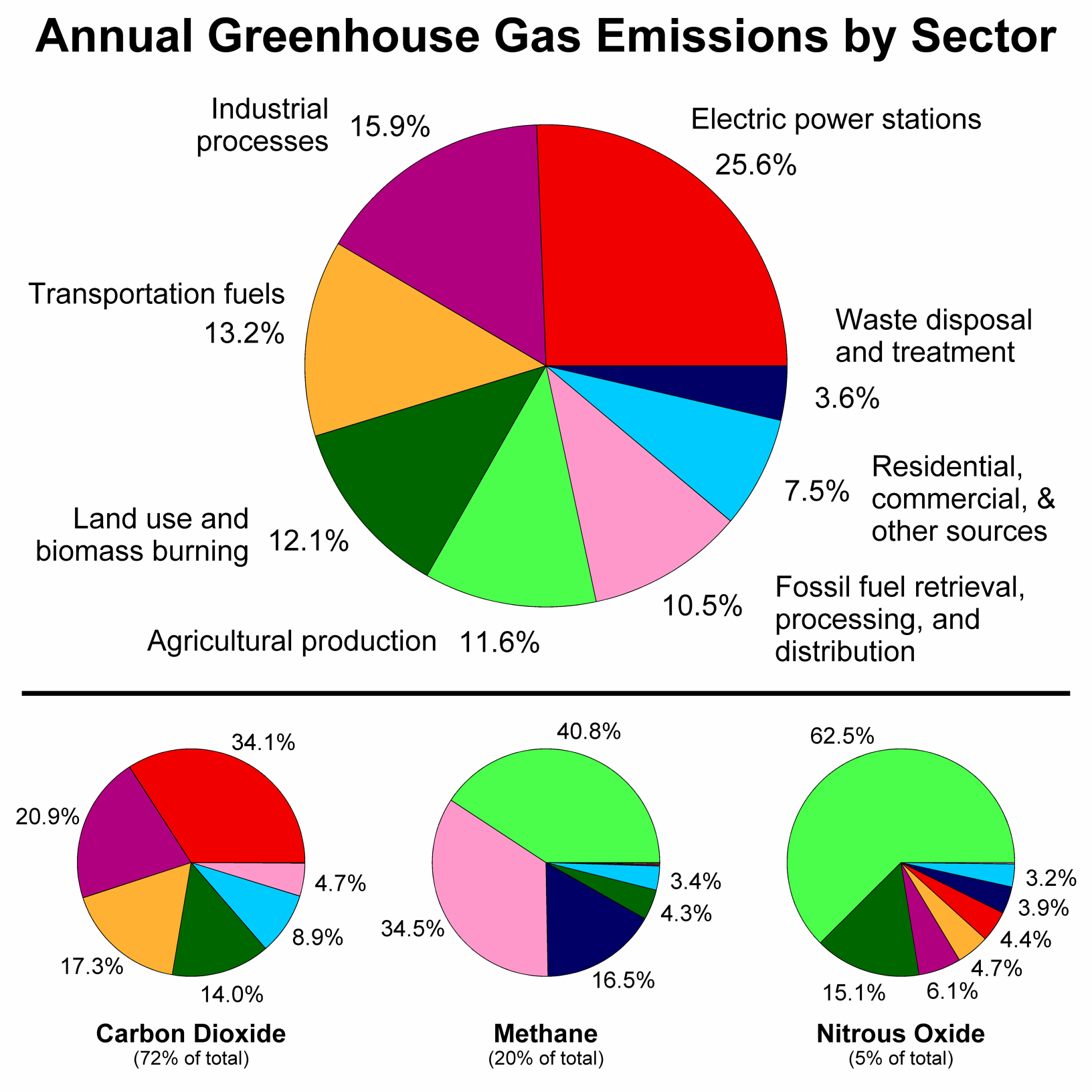
According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 Watts for every Earth as a closedup greenhouse would soon grow to be ghastly!Figure 121 Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Gas 04 Click for a text description of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas 04 Carbon dioxide/CO 2 fossilfuel use 566% Carbon dioxide/CO 2 (other) 28% Carbon dioxide/CO 2 (deforestation, decay of



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards spaceAlthough the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouse gasesA gas that absorbs heat within a planet's atmosphere, causing the greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases on earth include carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Thank you for visiting the Energy System Map If you're a young person between the age of 10, Student Energy invites you to participate in the Global Youth




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education
Without them, Earth's surface would average about 33 °C colder, which is about 59 °F below the present average of 14 °C (57 °F)" Greenhouse gas The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin The World Meteorological Organization's Greenhouse Gas Bulletin is published annually to report on the latest trends in atmospheric concentrations of the most important longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) climate change, carbon dioxide, greenhouse
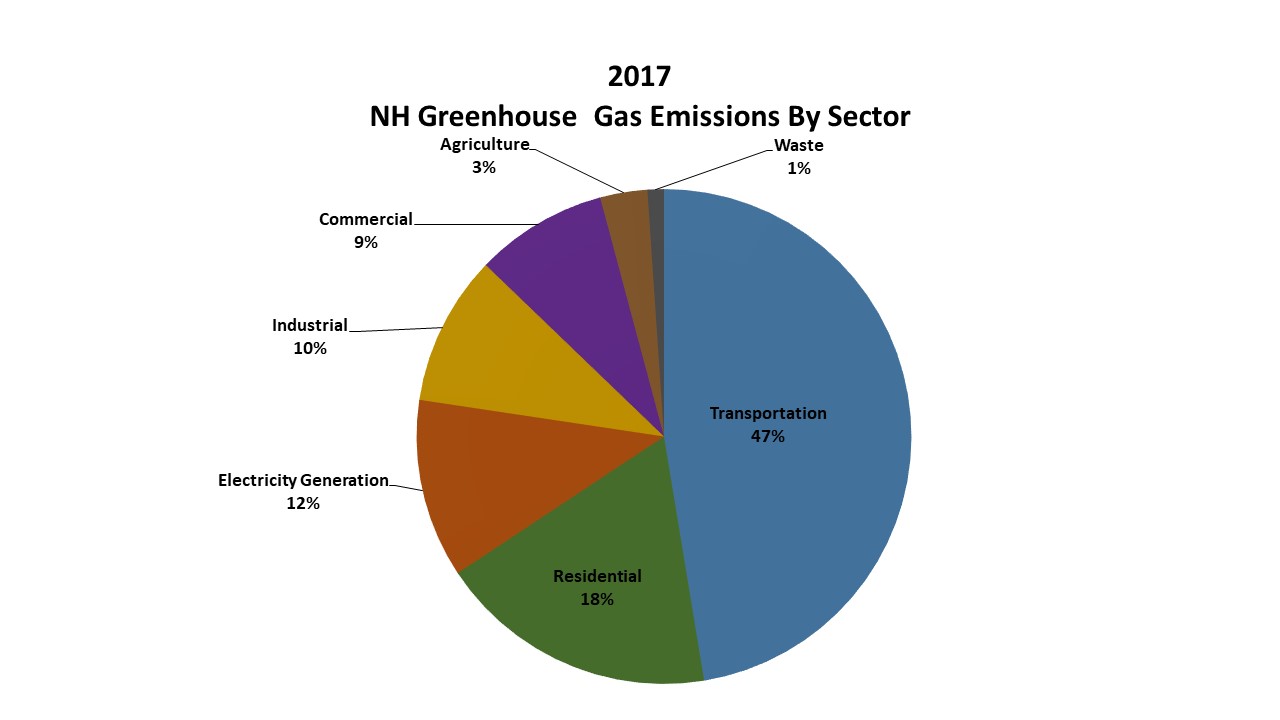



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research
Table of Contents Biofuels and the Carbon Cycle Indirect Land Use Impacts of Biofuels Differences among Biofuels Biofuels and the Carbon Cycle From the standpoint of humanreleased carbon dioxide, other greenhouse gas emissions, and contributions to climate change biofuels have one large advantage over gasoline, diesel and other fossil fuels TheChange and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and discusses the potential effects of the EIS Alternatives related to GHG emissions and climate change 371 Affected Environment Greenhouse Effect, Global Warming, and Climate Change Most of the energy that affects Earth's climate comes from the sun Some solar radiation is absorbed by Earth'sThe Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planet




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect What greenhouse gases do humans generate?Analyze their greenhouse gas emissions Then they will participate in a greenhouse experimental demonstration and finally demonstrate their knowledge of the greenhouse effect using a puzzle (Appendix A Diagram) Prior Knowledge & Skills • Introductory knowledge of the greenhouse effect • Data gathering skillsThe graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matter



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
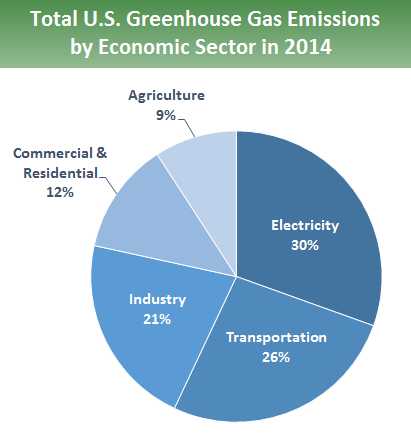
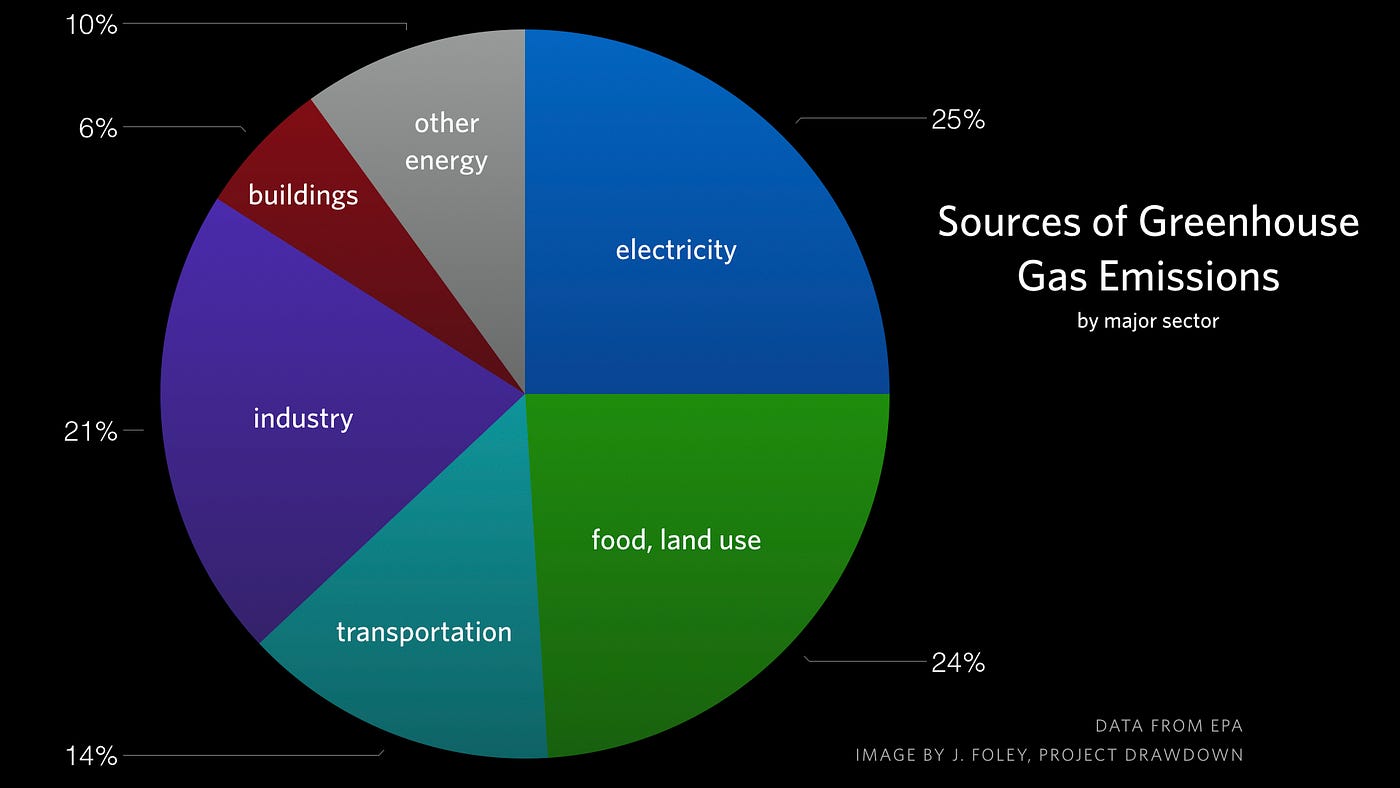
Portion of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States in 14 include transportation (26%) and industry (21%) Emissions from transportation primarily come Figure 3 Diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect TheThe primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth;




Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
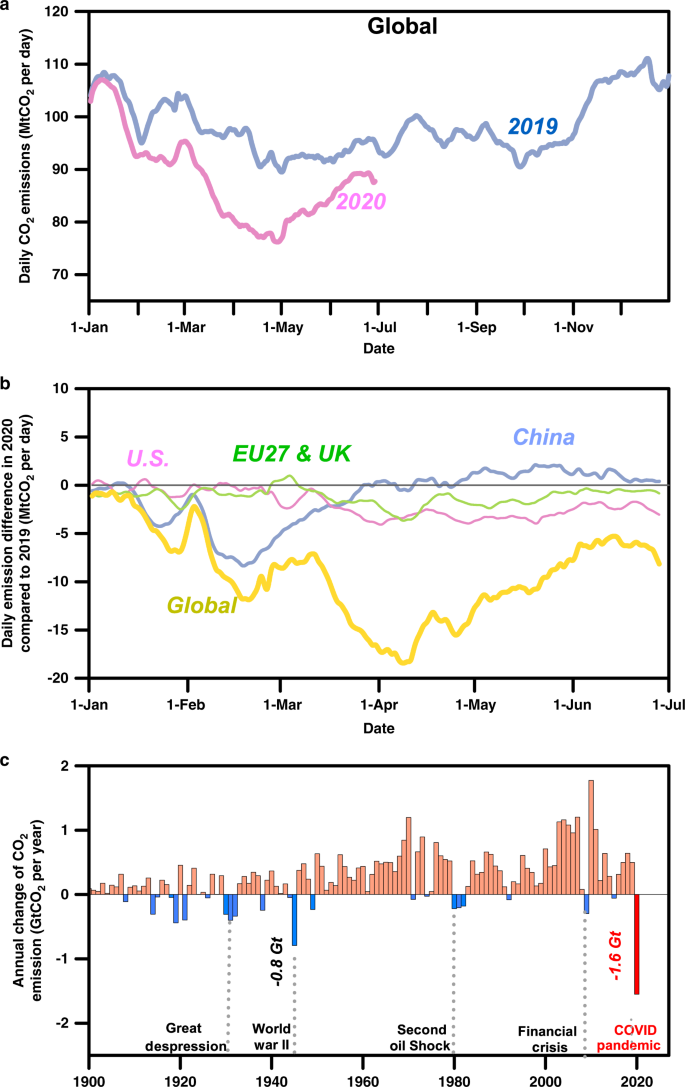



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications
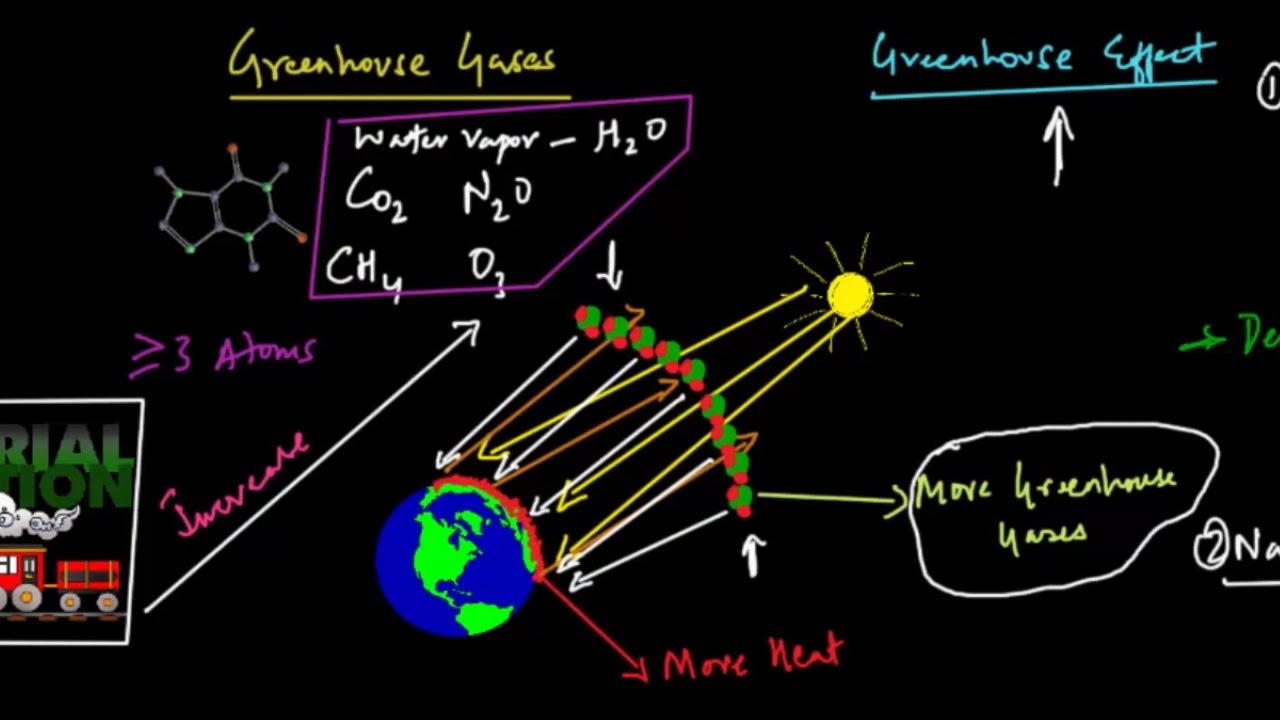



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network




Analysis Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The European Union Member States With The Use Of An Agglomeration Algorithm Sciencedirect
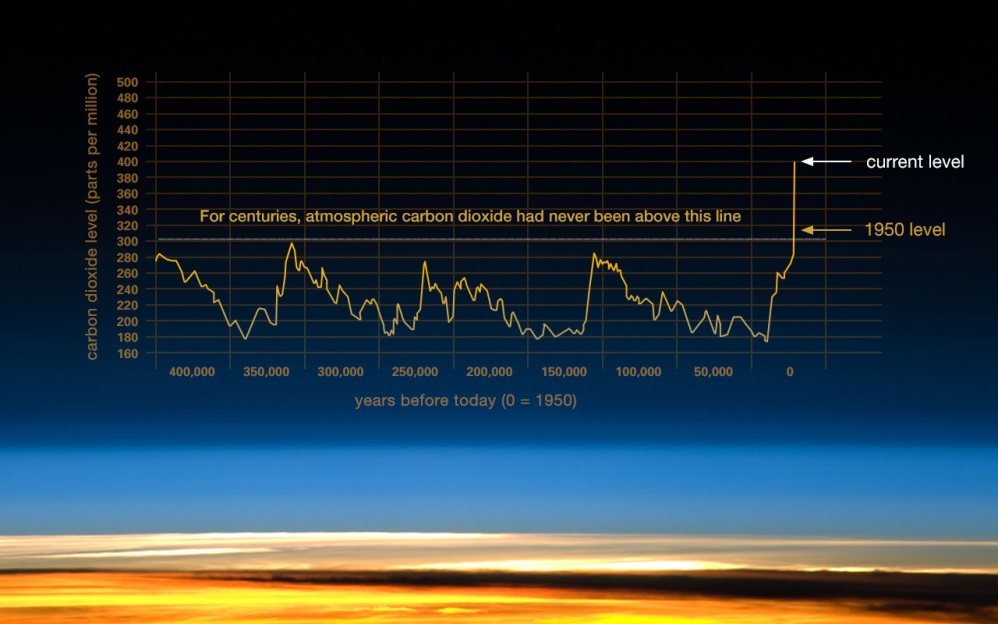



Causes And Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
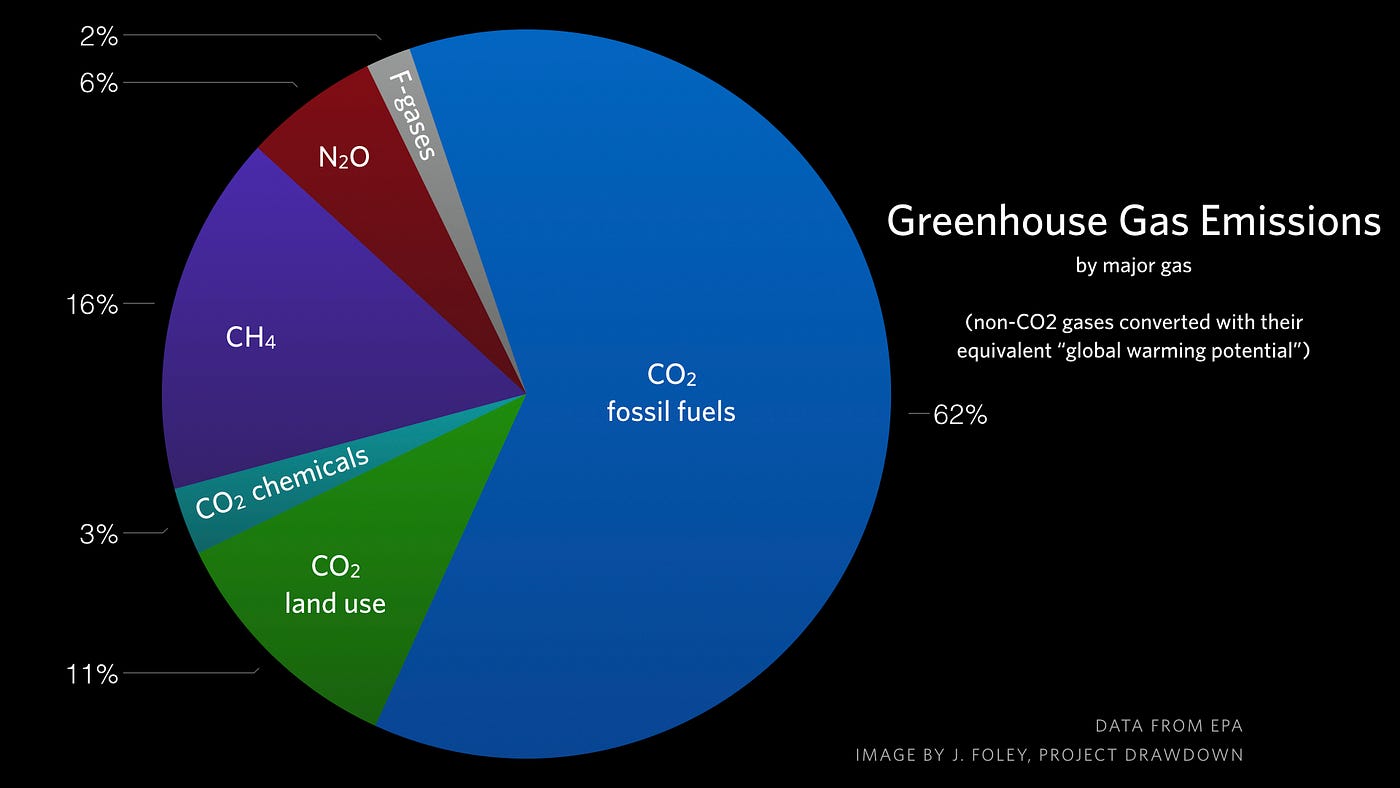



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
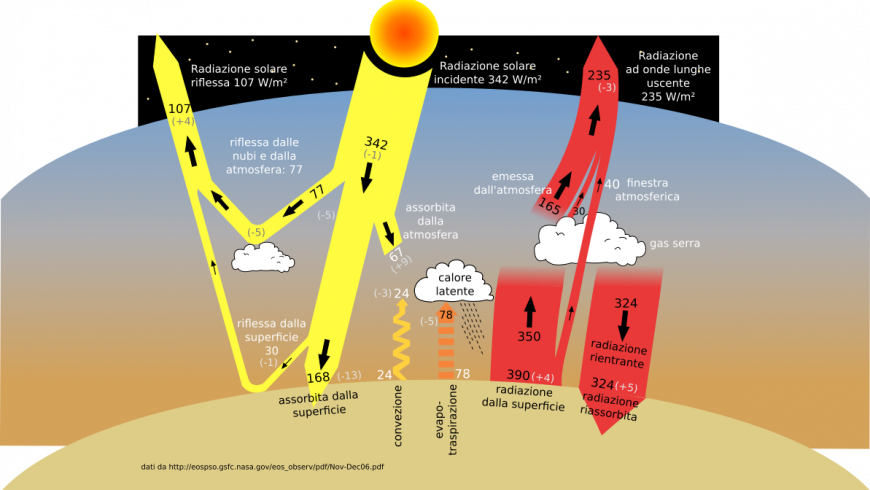



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
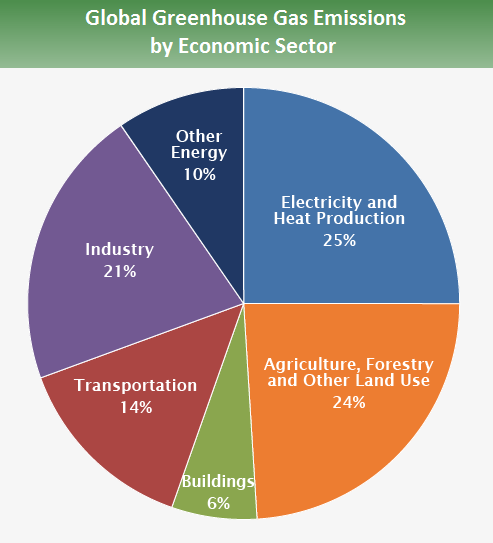



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Explained



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Www Extension Purdue Edu Extmedia Id Id 506 W Pdf
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox



1




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Major Greenhouse Gas Reductions Needed By 50 Ipcc Climate Central
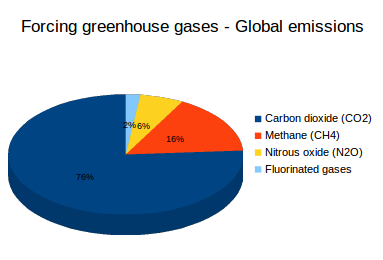



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Percentage Contribution Of Various Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Emissions Sources Climate Central




Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
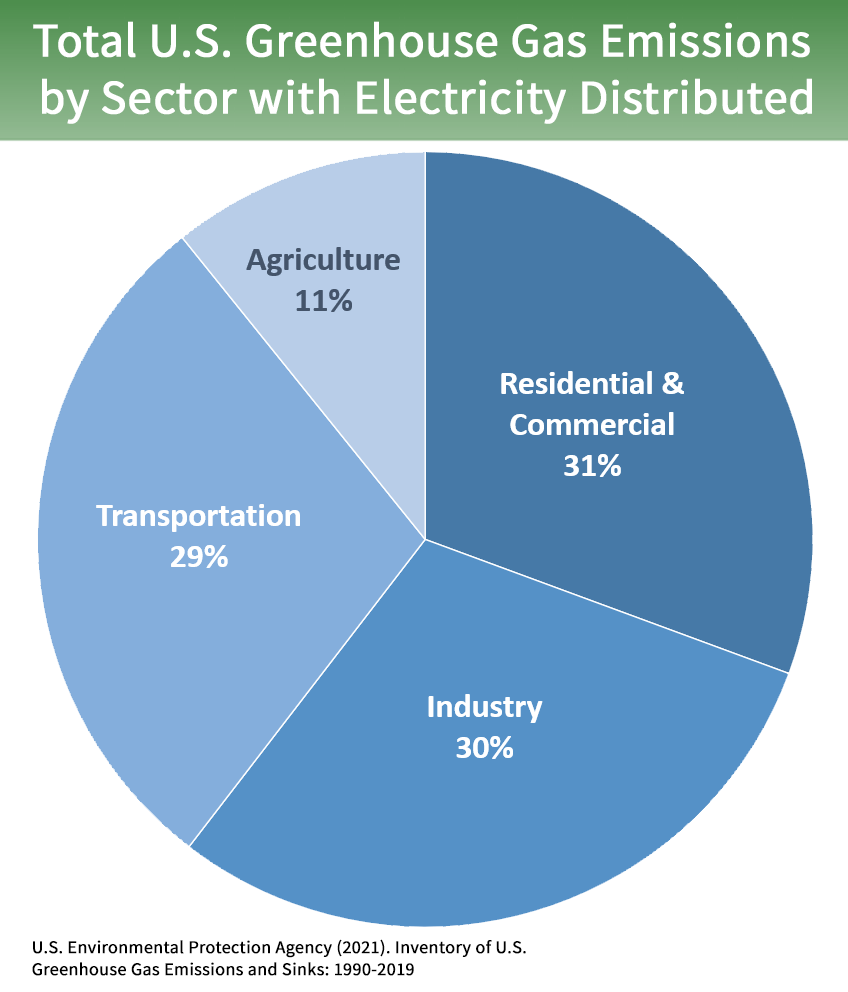



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
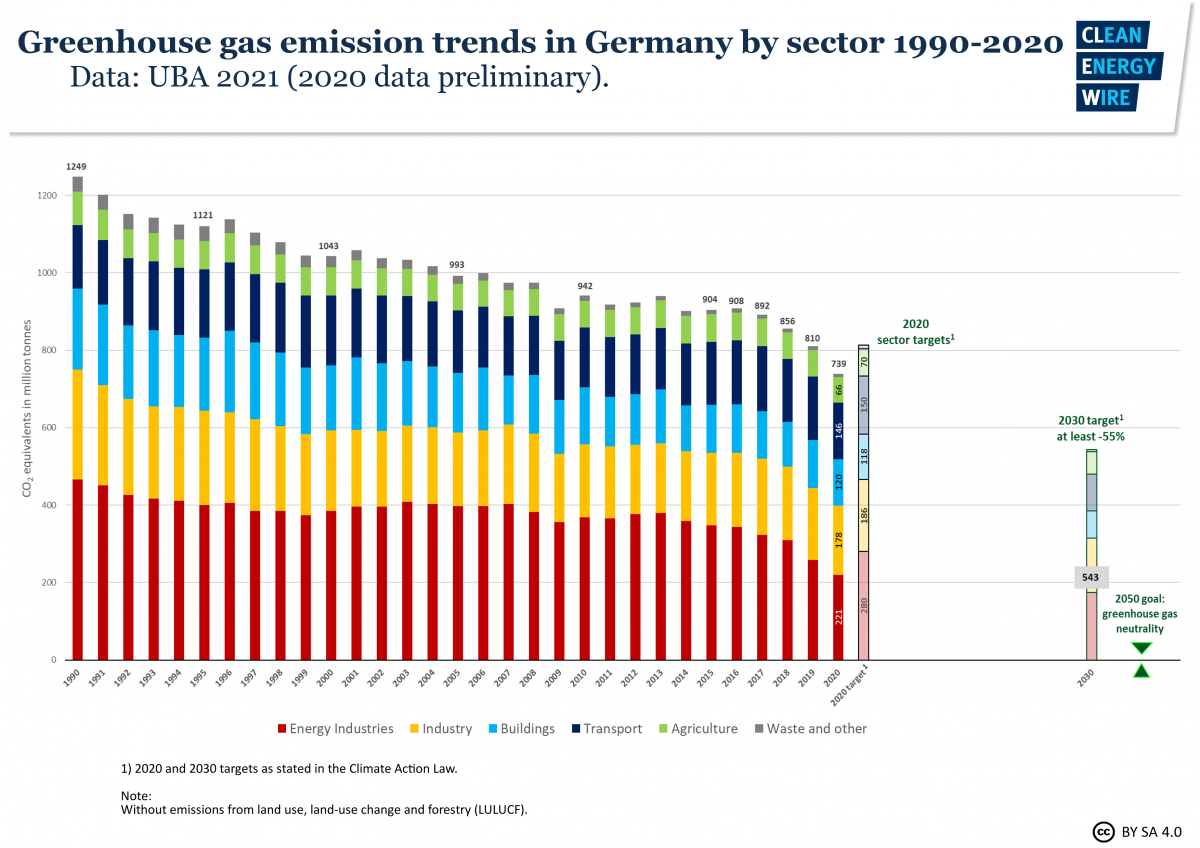



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




Climate Greenhouse Gases Sustainability
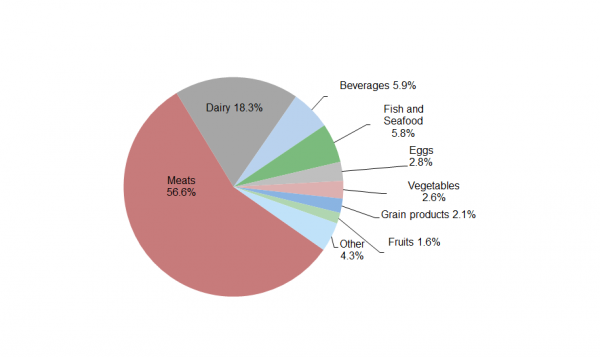



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Schematic Overview Of The Main Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Download Scientific Diagram



1



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Total Direct And Indirect Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Download Scientific Diagram




World Flow Chart Of Greenhouse Gases Illustrating The Emission Download Scientific Diagram
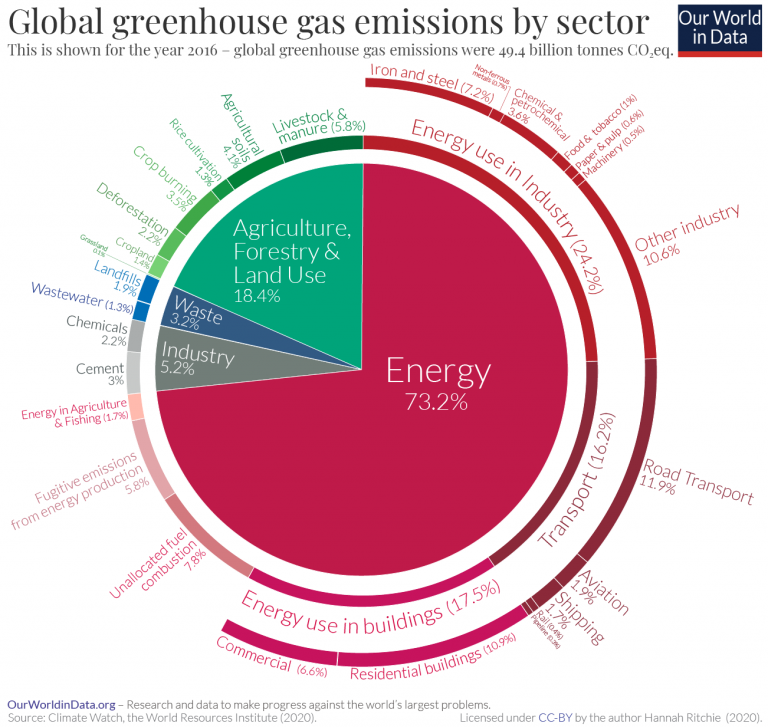



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data




Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Facts
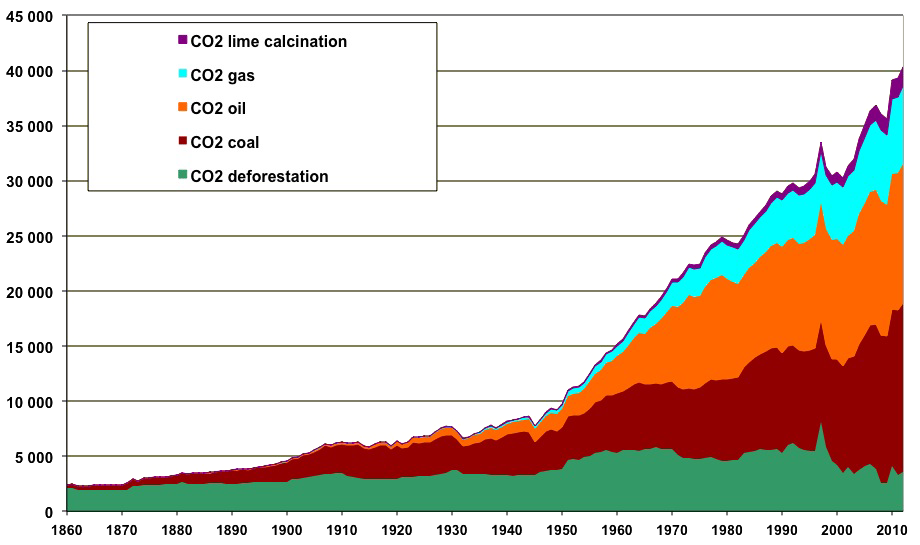



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Italki Ielts Writing Task 1 Answer 22 The Diagram Illustrates How Solar Energy Is Trapped By Greenhouse E
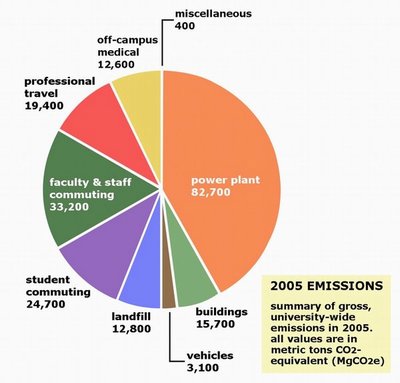



Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News
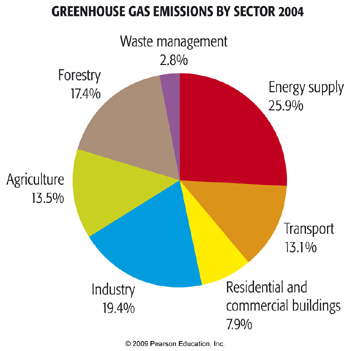



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg
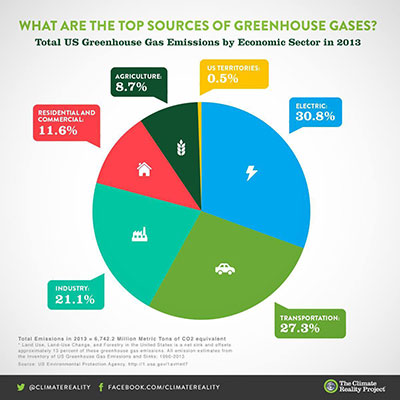



Agriculture Causes Less Emissions Than Transportation
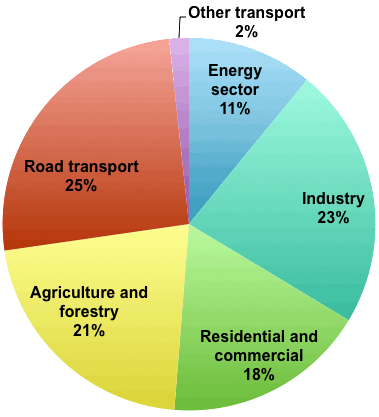



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
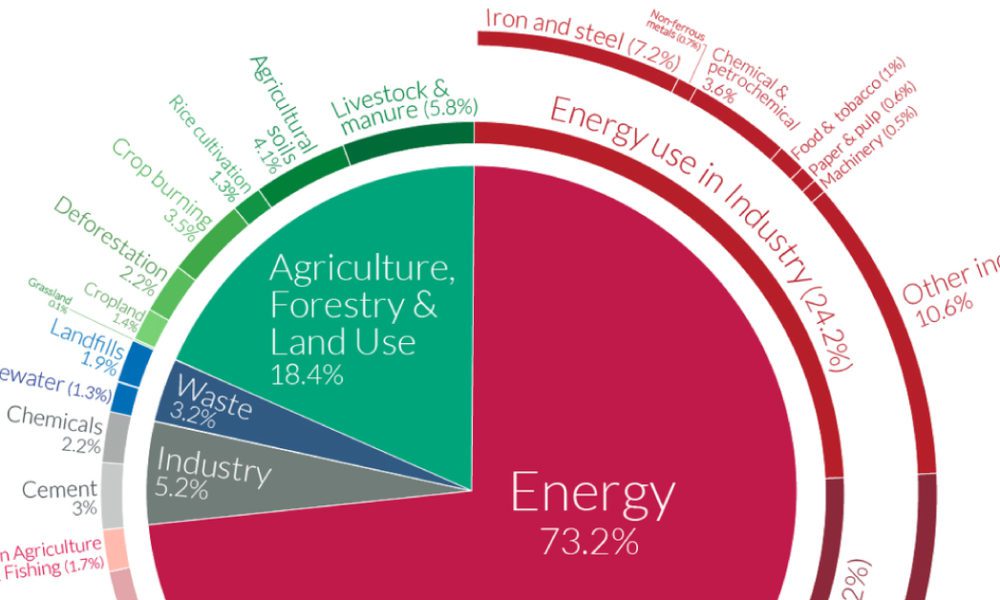



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Greenhouse Gases Transportation Benefit Cost Analysis
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox




27 Greenhouse Gases Ideas Greenhouse Gases Gas Greenhouse



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
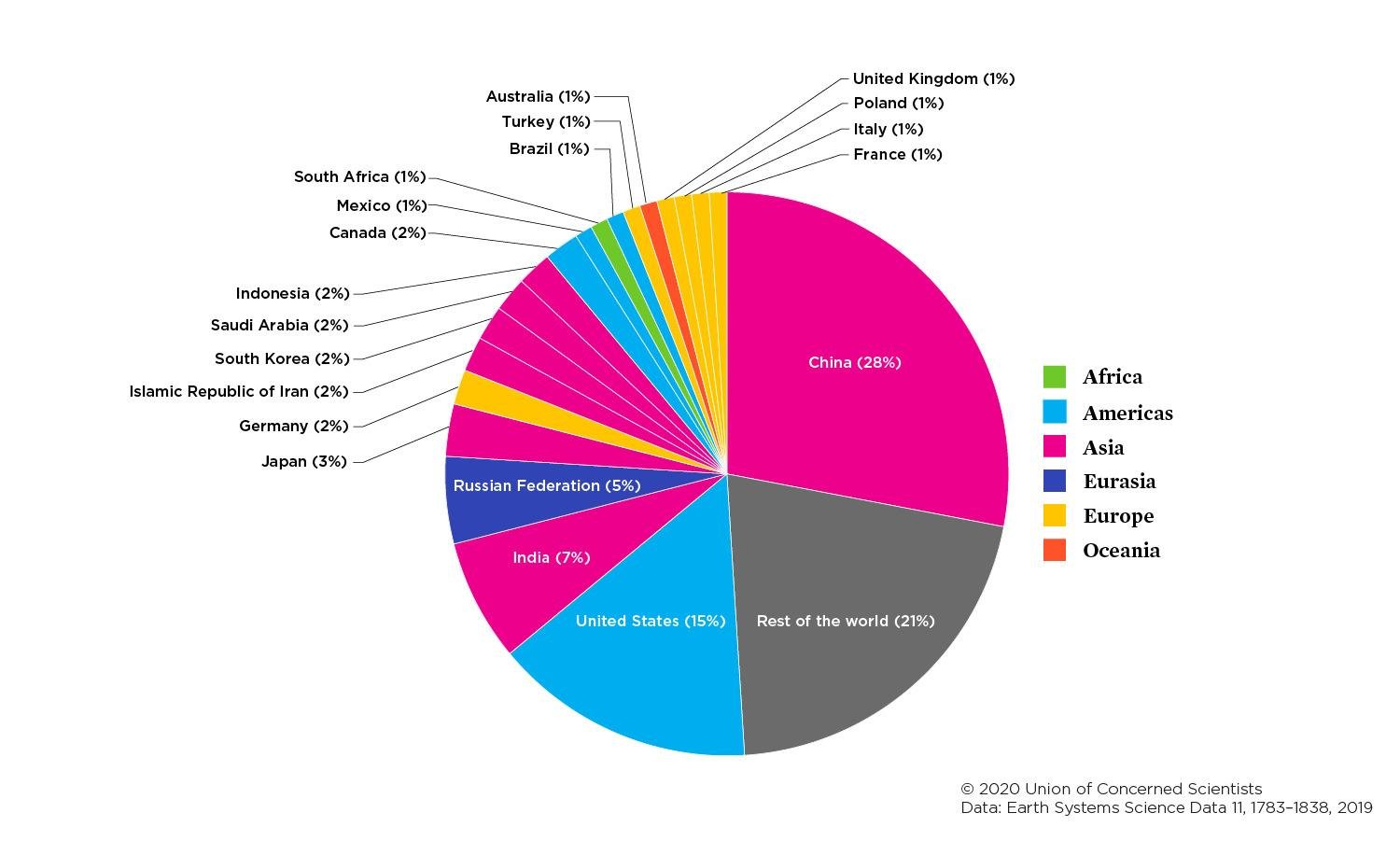



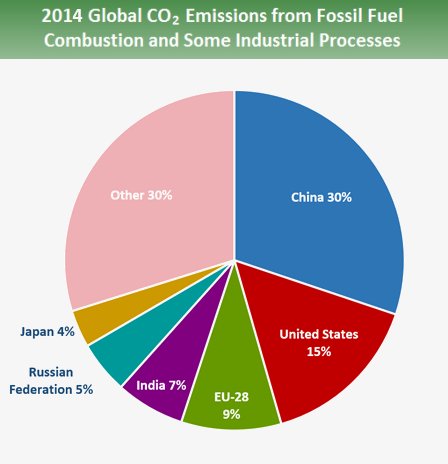
Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists



Bikes And Walking Transit Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Source
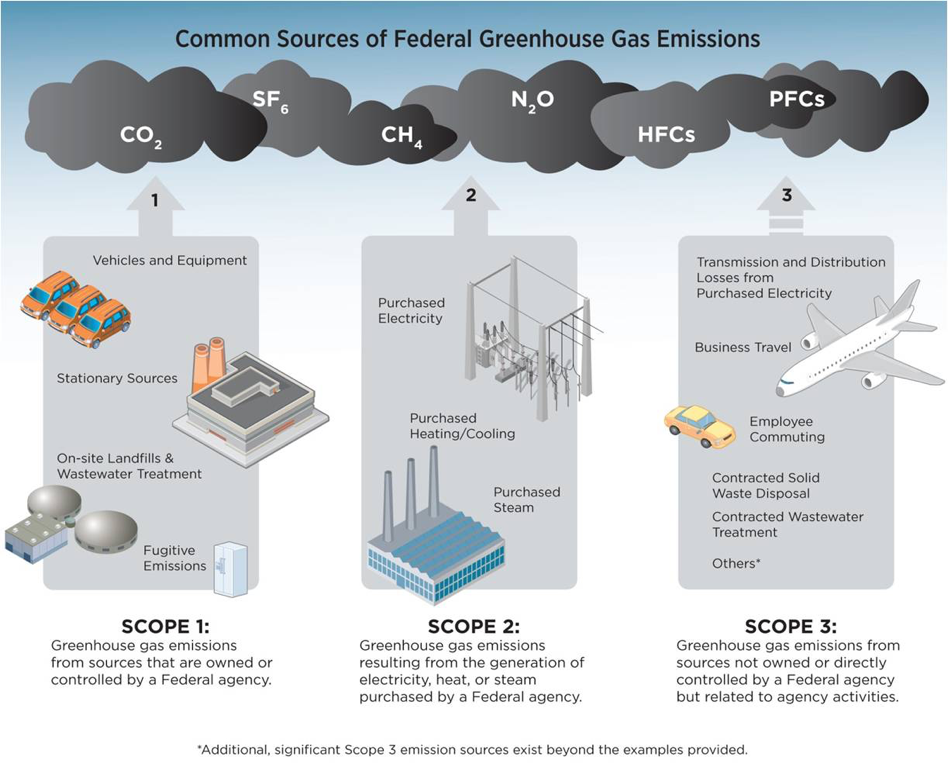



Greenhouse Gas Reduction Ghg Emissions




The Greenhouse Effect Mechanism
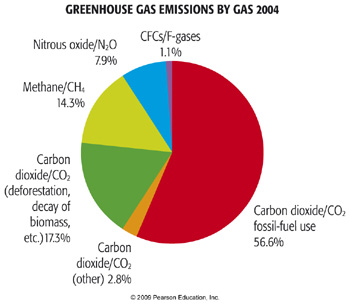



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿